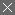価格+送料の最安値を表示しています。
公式・限定 2016年、クライスラーJEEP、コンパス
最安値
440,000
円
「 東京 」への最も安い送料
お届け先の都道府県は上部または左部から変更できます。離島、一部地域では別途料金が必要な場合があります。また、注文確認画面にて配送方法の変更が必要な場合があります。
車の買い替えのため短期出品です。
エンジン...ガソリンエンジン
国名...アメリカ
下道しか走ってませんがリッター12キロ。
車載カメラは取り外させて頂きます。
こちらは鹿児島県鹿児島市ですが、取引出来る方でしたら車関係でスムーズにやり取り出来る方お願い致します。
ボディタイプ...SUV・クロカン
中古購入で1年乗りました。
車検1年弱(令和6年4月)残ってます。
一度故障整備したのが、エレクトロニックスロットルコントロール (ETC) 警告灯のアラートが出てディーラーで直したばかりで好調です。
走行距離6.2万キロ
エンジン...ガソリンエンジン
国名...アメリカ
下道しか走ってませんがリッター12キロ。
型番.ABA-MK49
駆動式...2WD商品の情報
| カテゴリー: | 車・バイク・自転車>>>車>>>自動車本体 |
|---|---|
| 商品の状態: | やや傷や汚れあり |
| ブランド: | クライスラージープ |
車載カメラは取り外させて頂きます。
こちらは鹿児島県鹿児島市ですが、取引出来る方でしたら車関係でスムーズにやり取り出来る方お願い致します。
ボディタイプ...SUV・クロカン
中古購入で1年乗りました。
車検1年弱(令和6年4月)残ってます。
一度故障整備したのが、エレクトロニックスロットルコントロール (ETC) 警告灯のアラートが出てディーラーで直したばかりで好調です。
走行距離6.2万キロ
東京(離島除く)への最も安い配送方法での送料を表示しています ※注文確認画面にて配送方法の変更が必要な場合があります
価格+送料で安い順に表示しています。(上位100件のみ)
新品 96件
534,600
534,600
「 東京 」への最も安い送料
お届け先の都道府県は上部または左部から変更できます。離島、一部地域では別途料金が必要な場合があります。また、注文確認画面にて配送方法の変更が必要な場合があります。
455,400
455,400
「 東京 」への最も安い送料
お届け先の都道府県は上部または左部から変更できます。離島、一部地域では別途料金が必要な場合があります。また、注文確認画面にて配送方法の変更が必要な場合があります。
544,500
544,500
「 東京 」への最も安い送料
お届け先の都道府県は上部または左部から変更できます。離島、一部地域では別途料金が必要な場合があります。また、注文確認画面にて配送方法の変更が必要な場合があります。
455,400
455,400
「 東京 」への最も安い送料
お届け先の都道府県は上部または左部から変更できます。離島、一部地域では別途料金が必要な場合があります。また、注文確認画面にて配送方法の変更が必要な場合があります。
454,940
454,940
「 東京 」への最も安い送料
お届け先の都道府県は上部または左部から変更できます。離島、一部地域では別途料金が必要な場合があります。また、注文確認画面にて配送方法の変更が必要な場合があります。
382,200
382,200
「 東京 」への最も安い送料
お届け先の都道府県は上部または左部から変更できます。離島、一部地域では別途料金が必要な場合があります。また、注文確認画面にて配送方法の変更が必要な場合があります。
529,200
529,200
「 東京 」への最も安い送料
お届け先の都道府県は上部または左部から変更できます。離島、一部地域では別途料金が必要な場合があります。また、注文確認画面にて配送方法の変更が必要な場合があります。
382,200
382,200
「 東京 」への最も安い送料
お届け先の都道府県は上部または左部から変更できます。離島、一部地域では別途料金が必要な場合があります。また、注文確認画面にて配送方法の変更が必要な場合があります。
431,200
431,200
「 東京 」への最も安い送料
お届け先の都道府県は上部または左部から変更できます。離島、一部地域では別途料金が必要な場合があります。また、注文確認画面にて配送方法の変更が必要な場合があります。
中古 5件
中古 - 良い
548,800
548,800
「 東京 」への最も安い送料
お届け先の都道府県は上部または左部から変更できます。離島、一部地域では別途料金が必要な場合があります。また、注文確認画面にて配送方法の変更が必要な場合があります。
中古 - 良い
448,960
448,960
「 東京 」への最も安い送料
お届け先の都道府県は上部または左部から変更できます。離島、一部地域では別途料金が必要な場合があります。また、注文確認画面にて配送方法の変更が必要な場合があります。
中古 - 良い
378,300
378,300
「 東京 」への最も安い送料
お届け先の都道府県は上部または左部から変更できます。離島、一部地域では別途料金が必要な場合があります。また、注文確認画面にて配送方法の変更が必要な場合があります。
中古 - 良い
523,692
523,692
「 東京 」への最も安い送料
お届け先の都道府県は上部または左部から変更できます。離島、一部地域では別途料金が必要な場合があります。また、注文確認画面にて配送方法の変更が必要な場合があります。
中古 - 良い
542,640
542,640
「 東京 」への最も安い送料
お届け先の都道府県は上部または左部から変更できます。離島、一部地域では別途料金が必要な場合があります。また、注文確認画面にて配送方法の変更が必要な場合があります。
Shop of the Year 受賞店舗
設置対応可
商品設置サービス対応可能な商品
取付工事可
取付工事サービス対応可能な商品
組立対応可
商品組立サービス対応可能な商品
※各サービスの料金については商品ページでご確認ください
商品レビュー
2024年07月15日 13:51
使いやすい
子供が生まれた為、スプレータイプは避けたいと思い、こちらを見つけて購入。使い始めた日を書く所もありカーペットに挟んでおくだけ!とても管理しやすく重宝してます!
子供が生まれた為、スプレータイプは避けたいと思い、こちらを見つけて購入。使い始めた日を書く所もありカーペットに挟んでおくだけ!とても管理しやすく重宝してます!
2024年07月04日 05:57
アトピーの息子が使用し、布団に入ってからのムズムズがなくなったと喜んでいます。目に見えるものではございませんが、効果を実感しているようで、購入して良かったと思っています。リピートしたいと思っています。
2024年06月21日 20:00
これは良いです!
一緒に寝てる息子と私が、交互に何かに刺されてたので、レイコップをかけたり、シーツ洗ったり対応してきました。それでも、朝起きて暫くすると痒みが出て、小さな赤い噛まれたような跡が…
このダニマットを置いてから、二日目には何にも噛まれなくなり、私の嫌な不安は解消されました!
一緒に寝てる息子と私が、交互に何かに刺されてたので、レイコップをかけたり、シーツ洗ったり対応してきました。それでも、朝起きて暫くすると痒みが出て、小さな赤い噛まれたような跡が…
このダニマットを置いてから、二日目には何にも噛まれなくなり、私の嫌な不安は解消されました!
2024年06月18日 15:57
お値段以上
お手頃な価格だったので品質が心配でしたが、お値段以上のお品で満足しています。
ブラウンのお色も自然な感じで気に入りました♪
新居に使うのが楽しみです!!
お手頃な価格だったので品質が心配でしたが、お値段以上のお品で満足しています。
ブラウンのお色も自然な感じで気に入りました♪
新居に使うのが楽しみです!!
製品詳細情報
|
発売日
|
2024/07/27
|
|---|---|
|
カテゴリー:
|
車・バイク・自転車>>>車>>>自動車本体
|
|
商品の状態:
|
やや傷や汚れあり
|
|
ブランド:
|
クライスラージープ
|
関連ジャンル
スマホ・タブレット・パソコン
家具・インテリア
ハンドメイド・手芸
フラワー・ガーデニング
ベビー・キッズ
スポーツ
ゲーム・おもちゃ・グッズ
ホビー・楽器・アート
DIY・工具
商品価格ナビについての注意
・商品をご購入頂く際には、リンク先の商品情報をご確認の上でお願いいたします。ページ内の製品とリンク先のショップの商品が異なる場合、
こちら
までご連絡ください。
・商品について重要な情報が記載されている場合や、価格・送料・在庫表示等が異なる場合がございます。ご購入前に必ず商品ページをご確認ください。
・最安価格(税込)は在庫あり・注文可能商品における最安価格です。
・この検索結果を元に商品ご購入される際には、ご自身でも各商品の詳細についてご確認ください。
・各製品の情報は各メーカー企業・データ販社などから提供されたデータに基づき表示している参考情報です。各ショップが実際に販売している商品やパッケージの情報とは詳細が異なる場合がありますのでご注意ください。より正確な情報は、各ショップにお問い合わせください。
・検索結果によって行われる商品取引を楽天市場が保証することはございません。
・画像は代表製品・代表カラーを共用しております。
・実際の製品イメージ、カラーとは異なる場合があります。
・掲載されている情報はメーカー各社により予告なく変更される場合がございます。
・商品情報の更新は定期的に行われているため、実際の商品ページの内容(価格、在庫表示等)とは異なる場合がございます。ご注意ください。
・レビューには、サイズや色、数量など複数の種類がある商品はすべての種類を一つの商品のレビューとして一覧表示し、総合評価を算出しています。
・ショップレビューは、「みんなのお買い物レビュー」の集計を元に表示しておりますが、定期的に更新しているため、リンク先の表示内容と異なる場合がございますのでご了承ください。
・「獲得ポイント」には、注文商品の税込価格の1%分を元に、ポイント倍付けキャンペーンなどの付与率変動を考慮して計算し表示しています。ショップの方針によって誤差が生じる可能性がありますので、正確な獲得ポイント数は注文画面にてご確認下さい。
・購入金額が100円(税込)に満たないお買い物はポイント対象外となります。
・クーポンの有効期間中であっても利用枚数の合計が先着人数に達した時点でクーポンは利用できなくなりますのでご注意下さい。(獲得後であっても利用時点ですでに上限枚数を利用されている場合は、お買い物かごでのクーポンの表示はされません)
・獲得したクーポンを利用せずに商品をご購入されますと、通常価格でご購入いただくこととなりますのでご注意ください。
ご意見・ご要望
ページについてのご意見・ご要望をお聞かせください。今後のサイト改善の参考にさせていただきます。